cSpan-Structure-Sequence Based Analysis for Identification Conservation Regions in Proteins
Sequence conservation in structurally conserved “span” regions is a quantitative measure of residue conservation in local structure context
Background
In order to identify new, unknown proteins associated with viruses, such as COVID-19, it is easiest to start by identifying structurally related proteins. LLNL scientists have created tools that identify structurally related proteins and their relevant residues, called cSpan.
Technology Overview
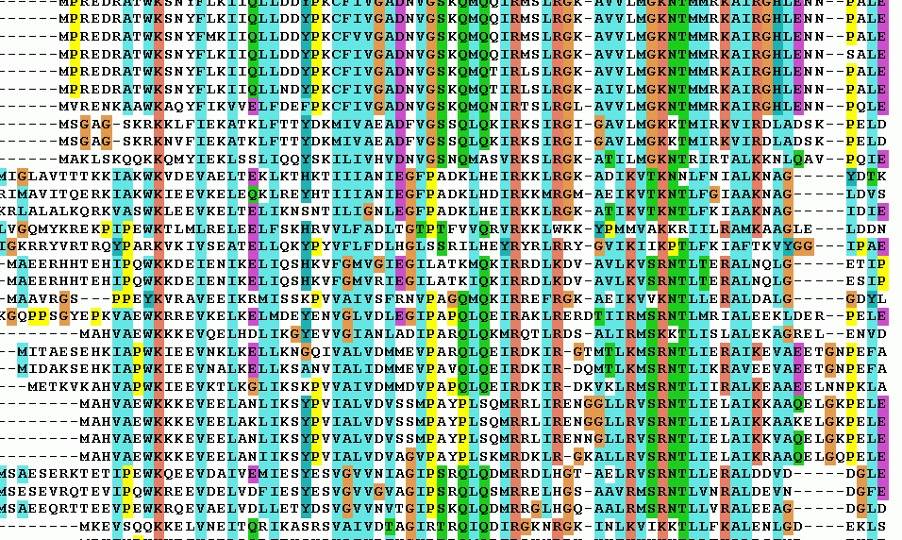
The cSpan (sequence conservation in structurally conserved “span” regions) calculation is a quantitative measure of residue conservation in local structure context. It is used to identify residues on a protein that are conserved with respect to a set of structurally related proteins. A set of protein structures (consisting of a reference protein, and any number of related proteins) is aligned using the LGA (local-global alignment) software (see Local-Global Alignment: A Method for Finding 3D Similarities in Protein Structures). A multiple structure-based residue-residue correspondence (or “multiple structure-based sequence alignment”, MSSA) is extracted from the structural alignments and corresponding (structurally aligned) residues are compared. Each residue in the reference protein is scored (assigned cSpan value) according to how similar it is to each corresponding residue in the set of related proteins. The reference protein’s cSpan values can be plotted vs. the residue number to identify conserved sub-sequences, consisting of high-cSpan residues. Additionally, they can be projected onto a 3-D structure or model to assist in identification of features conserved in sequence and structure.
Applications
The cSpan algorithm (combined structure- and sequence-based analyses) can be used to identify and characterize surface features of interest in development of diagnostic reagents, therapeutics, or vaccines, and to functionally annotate pathogen proteins.
# IL11776